Modern injection and diesel engines use control systems with many sensors that monitor dozens of parameters. Among the sensors, a special place is occupied by the phase sensor, or the camshaft position sensor. Read about the functions, design and operation of this sensor in the article.
What is a phase sensor
Phase sensor (DF) or camshaft position sensor (DPRV) is a sensor of the control system for injection gasoline and diesel engines that monitors the position of the gas distribution mechanism. With the help of DF, the beginning of the engine cycle is determined by its first cylinder (when TDC is reached) and a phased injection system is implemented. This sensor is functionally connected to the crankshaft position sensor (DPKV) - the electronic engine management system uses the readings of both sensors, and, based on this, generates pulses for fuel injection and ignition in each cylinder.
DFs are used only on gasoline engines with distributed phased injection and on some types of diesel engines. And it is thanks to the sensor that the very principle of phased injection is most easily implemented, that is, fuel injection and ignition for each cylinder, depending on the engine operating mode. There is no need for DF in carburetor engines, since the fuel-air mixture is supplied to the cylinders through a common manifold, and the ignition is controlled using a distributor or a crankshaft position sensor.
DF is also used on engines with a variable valve timing system. In this case, separate sensors are used for the camshafts that control the intake and exhaust valves, as well as more complex control systems and their operating algorithms.
Design of phase sensors
Currently, DF based on the Hall effect is used - the occurrence of a potential difference in a semiconductor wafer through which direct current flows when it is placed in a magnetic field. Hall effect sensors are implemented quite simply. It is based on a square or rectangular semiconductor wafer, to the four sides of which contacts are connected - two input, for supplying direct current, and two output, for removing the signal. For convenience, this design is made in the form of a chip, which is installed in the sensor housing along with the magnet and other parts.
There are two design types of phase sensors:
-Slotted;
- End (rod).
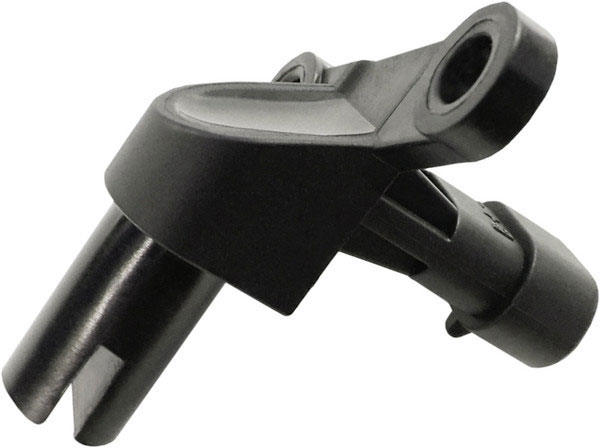

Slit sensor
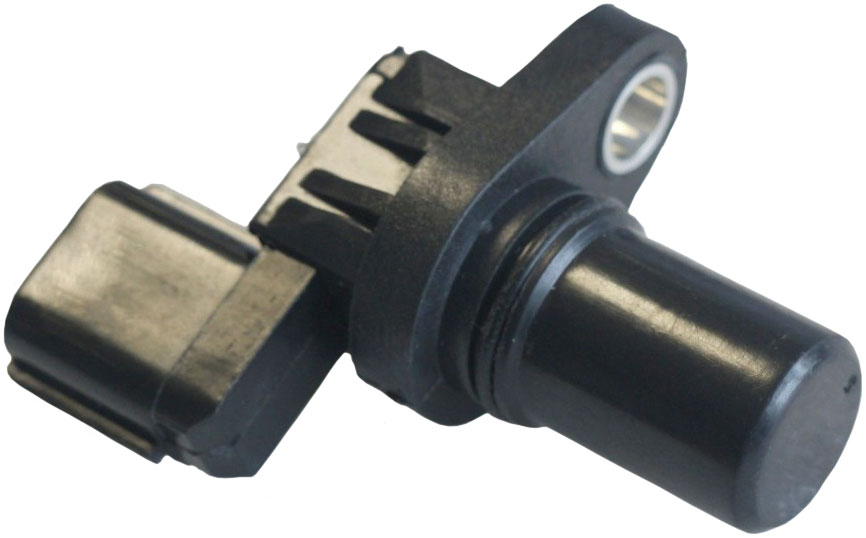

End sensor
The slotted phase sensor has a U-shape, in its section there is a reference point (marker) of the camshaft. The body of the sensor is divided into two halves, in one there is a permanent magnet, in the second there is a sensitive element, in both parts there are magnetic cores of a special shape, which provide a change in the magnetic field during the passage of the benchmark.
The end sensor has a cylindrical shape, the camshaft reference point passes in front of its end. In this sensor, the sensing element is located at the end, above it is a permanent magnet and magnetic cores.
It should be noted here that the camshaft position sensor is integral, that is, it combines the signal sensing element described above and a secondary signal converter that amplifies the signal and converts it into a form convenient for processing by the electronic control system. The transducer is usually built directly into the sensor, which greatly simplifies the installation and configuration of the entire system.
Working Principle of Phase Sensor
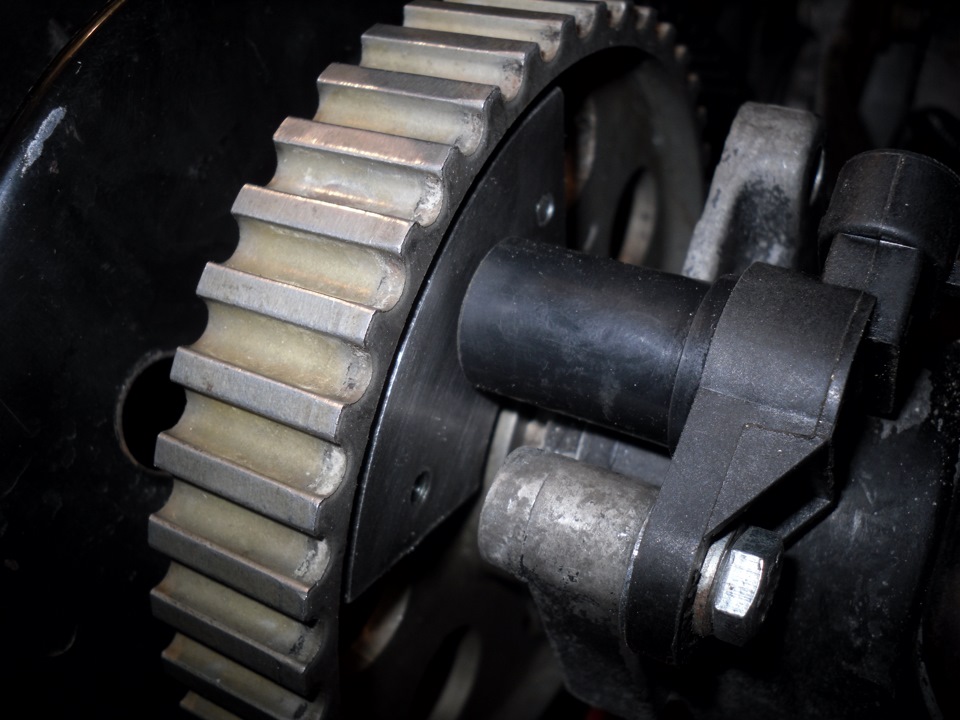

The phase sensor is paired with a master disc mounted on the camshaft. This disc has a reference point of one design or another, which passes in front of the sensor or in its gap during engine operation. When passing in front of the sensor, the reference point closes the magnetic lines coming out of it, which leads to a change in the magnetic field crossing the sensitive element. As a result, an electrical impulse is generated in the Hall sensor, which is amplified and changed by the converter, and fed to the electronic engine control unit.
For slotted and end sensors, master discs of different designs are used. Paired with slotted sensors, a disk with an air gap works - a control pulse is formed when passing this gap. Paired with an end sensor, a disk with teeth or short benchmarks works - a control impulse is formed when the benchmark passes.
The phase sensor is paired with a master disc mounted on the camshaft. This disc has a reference point of one design or another, which passes in front of the sensor or in its gap during engine operation. When passing in front of the sensor, the reference point closes the magnetic lines coming out of it, which leads to a change in the magnetic field crossing the sensitive element. As a result, an electrical impulse is generated in the Hall sensor, which is amplified and changed by the converter, and fed to the electronic engine control unit.
For slotted and end sensors, master discs of different designs are used. Paired with slotted sensors, a disk with an air gap works - a control pulse is formed when passing this gap. Paired with an end sensor, a disk with teeth or short benchmarks works - a control impulse is formed when the benchmark passes.
Post time: Aug-24-2023
